Vitamin C & Immunity
Photo by Karolina Grabowska from Pexels
We’ve all heard about vitamin C, particularly in the winter. It’s often associated with cold prevention and natural remedies. But what is the link between vitamin C and our immune system? And can it really prevent a cold? Keep reading to find out more!
What is vitamin C & why do we need it?
Vitamin C - a.k.a. ascorbic acid - is a water-soluble vitamin which is found in many foods. Vitamin C is referred to as an essential vitamin. This is because our bodies cannot make it or store, so we need to get it from food every day.
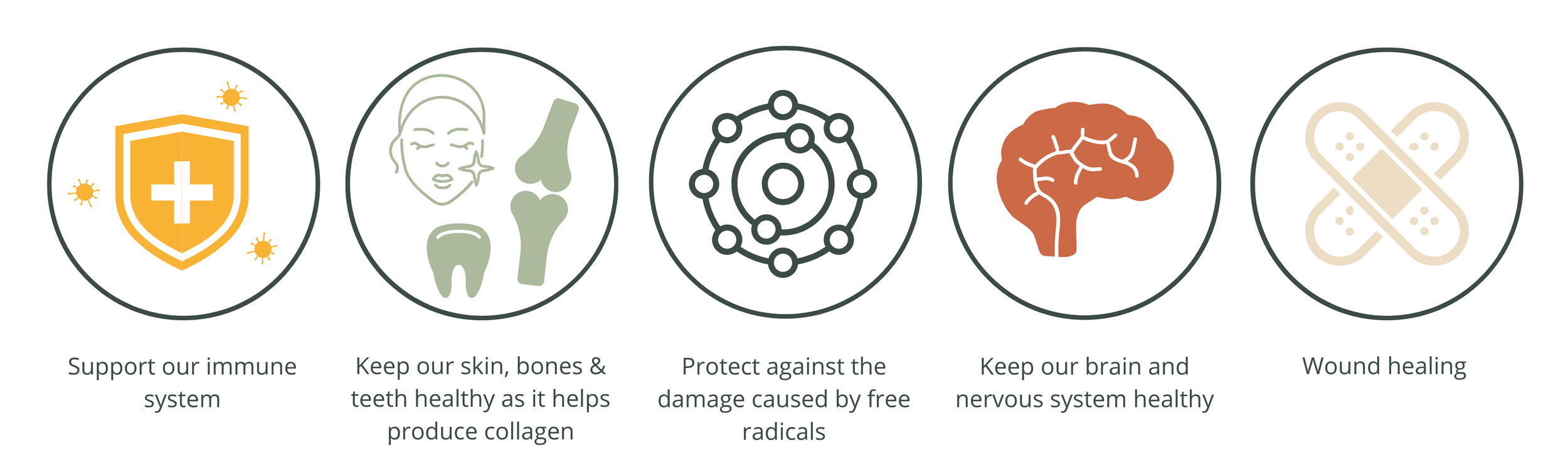
We need vitamin C to support our immune system, keep our skin, bones, and teeth healthy as it helps produce collagen, protect us against the damage caused by free radicals, keep our brain and nervous system healthy, and help with wound healing. Vitamin C also helps our bodies absorb iron from plant sources - non-haem iron.
What foods are a source of vitamin C?
Fruit and vegetables are the best source of vitamin C, so it’s important we eat a wide variety.
Some of the best sources of vitamin C are:
Fruits:
Kiwi
Berries - strawberries, blackcurrants, elderberries, raspberry, blackberry
Citrus Fruit - oranges, lemon, grapefruit, clementines
Pineapple
Guava
Papaya
Lychee
Mango
Cherries
Vegetables
Bell peppers
Broccoli
Cauliflower
Cabbage
Brussel sprouts
Kale
Potatoes
Some herbs - parsley, chives, horseradish & fenugreek leaves - are also rich in vitamin C, but as we do not eat them in large amounts, they don’t really increase our intake.
Tip: To get the most vitamin C out of these foods, eat them as soon as possible and don’t overcook them as they can lose vitamin C when heated or stored for long periods of time.
How much vitamin C?
Since we cannot store vitamin C in our bodies, or make it on our own, we need to get it from our food every single day. This can be achieved by eating a balanced diet.
For healthy adults - over the age of 18 - it is recommended we have between 95 mg for women and 110 mg for men of vitamin per day.
During pregnancy, it is recommended to increase that amount to 105 mg of vitamin C and during lactation to 155 mg of vitamin C.
What is the link between vitamin C & immunity?
Vitamin C plays an important part in supporting our immune system, which helps us fight against infection.
Vitamin C helps promote the production of white blood cells - leukocytes - which are cells of the immune system that protect us. It helps with wound healing and keeps skin healthy, which is one of our body’s first barriers of defence. Vitamin C is also a powerful antioxidant, meaning it protects us against oxidative damage caused by free radicals.
It is often thought that vitamin C can help prevent infections like colds, however, that’s not exactly the case. When we have a cold, supplementing with vitamin C can help reduce symptoms and help us recover faster, but unfortunately, it can’t help us prevent it.
Remember that too high doses of vitamin C - through supplementation for example - can upset our stomach and gut, causing stomach pains, diarrhoea or flatulence.
What’s the take-home?
We need vitamin C in our food every single day as we cannot make it or store it.
Vitamin C plays a number of important roles, including supporting immunity, skin health and wound healing.
Fruit and vegetables are the best source of vitamin C, like kiwis, bell peppers, berries, or broccoli.
Vitamin C supplementation cannot help us prevent a cold, but it can help speed-up recovery and reduce symptoms.
Check out these other Nutrition & Lifestyle posts…
References
British Nutrition Foundation. Healthy Sustainable Diets - Vitamins and Minerals. 2021. Retrieved December 15, 2022, from https://www.nutrition.org.uk/healthy-sustainable-diets/vitamins-and-minerals/
National Health Service (NHS). Vitamins and Minerals - Vitamin C. Retrieved December 15, 2022, from https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/vitamins-and-minerals/vitamin-c/
European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Scientific Opinion on Dietary Reference Values for vitamin C. EFSA Journal 2013;11(11):3418.
Calder P.C. Feeding the immune system. Proc Nutr Soc. 2013; 72(3):299-309. doi: 10.1017/S0029665113001286.
Iddir M., Brito A., Dingeo G., Fernandez Del Campo S.S., Samouda H., La Frano M.R., Bohn, T. Strengthening the Immune System and Reducing Inflammation and Oxidative Stress through Diet and Nutrition: Considerations during the COVID-19 Crisis. Nutrients. 2020, 12, 1562. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12061562
Childs C.E., Calder P.C., Miles E.A. Diet and Immune Function. Nutrients. 2019. 16;11(8):1933. doi: 10.3390/nu11081933.